Blockchain technology in Advanced Manufacturing: Transforming Efficiency, Transparency and Trust.
DTAM Article
In the ever-evolving landscape of advanced manufacturing, blockchain technology is emerging as a game-changer. This groundbreaking technology, initially associated with cryptocurrencies, has now found its place on the manufacturing industry, promising to revolutionize the way we conceive, produce, and deliver products. In this article, we will provide an overview about the potential of blockchain in advanced manufacturing, showcasing its major capabilities.
Blockchain technology in a nutshell
At its core, blockchain is a revolutionary technology that operates as a decentralized and immutable ledger. Unlike traditional databases where information is stored in a centralized manner, blockchain stores data in a chain of linked blocks across a network of computers. Each data entry, such a transaction or a smart contract (a self-executing contract) is stored inside a data block, which is cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming a continuous chain that is the same for all participants in the network. Once information is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes nearly impossible to alter or delete, ensuring its permanence and security.
This trust is the main characteristic of blockchain technology, making it a valuable solution for industries like advanced manufacturing, where transparency, precision, and accountability are essential. Now, let's explore how blockchain can be used in the advanced manufacturing ecosystem.
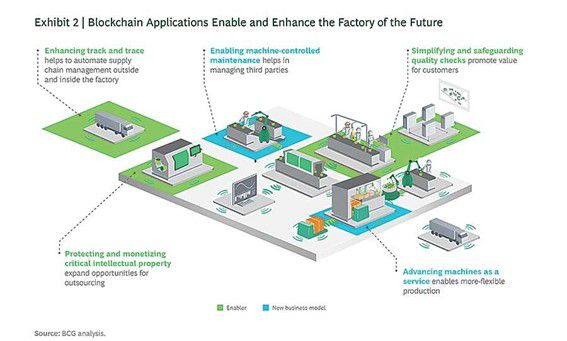
Transparent Supply Chains
Imagine a manufacturing process where the journey of every component, from raw materials to finished products, is visible and unchangeable. Blockchain makes this possible by creating an immutable ledger that records each step of the supply chain. Thanks to this increased transparency, manufacturers can trace the origins of materials, verify their quality, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Blockchain's potential in supply chain management extends beyond mere visibility. It mitigates the risks associated with counterfeit materials and parts, ensuring that only authentic components enter the production line, which is vital in industries such as pharmaceutical or aerospace. This not only safeguards the integrity of the final product but also enhances the trust between manufacturers and suppliers and facilitates quality assurance and auditing processes, as the auditors gain access to an immutable record of manufacturing processes and product history.
Intellectual Property Protection and Monetization
A company can use blockchain technology to secure their Intellectual Property (IP) rights, as we see in Bernstein Technologies web service, which allows users to register Intellectual Property in a blockchain, creating a certificate that proves its existence and ownership.
Blockchain can also be used to monetize a company´s digital assets while keeping their IP secure. Here is how it works: Imagine machines in an additive manufacturing facility connected to a blockchain that creates parts using the design files stored in a blockchain.
In order to monetize these design files (IP), the owner company would employ a smart contract powered licensing model to grant access to the information through the blockchain to the company using (and therefore paying for) the design files. This would guarantee access to the design file to third parties while preserving the IP of the owner company.
Smart Contracts for Efficiency
Smart contracts can significantly enhance the precision and timing in an advanced manufacturing facility by automating various aspects of manufacturing agreements and reducing the need for intermediaries. Let´s use machine maintenance as an example: to facilitate maintenance services from external providers, a user company can store service agreements and installation instructions for their machinery in the blockchain. When a machine needs maintenance, it will send a request for service to the maintenance company and create a smart contract for the services needed, allowing payment for the maintenance work or piece replacement to be made automatically once the service was provided.
In conclusion, the integration of blockchain technology into advanced manufacturing, promises to transform the sector by enabling transparent supply chains, streamlined operations, and enhanced trust among stakeholders. As the manufacturing sector evolves and becomes more complex and technologically driven, embracing blockchain technology can provide a leg up for those who are looking for competitiveness, security and innovation.
Sources:
1. Blockchain in the Factory of the Future, Daniel Küpper (Assembly), May 15, 2020.
2. Blockchain in Manufacturing: Challenges of Adoption and Use Cases, Infopulse, originally published on March 13, 2019 and updated on January 17, 2023.
3. Bernstein: Digital Intellectual Property protection, Web3 solution to secure and leverage intellectual property assets.
4. Blockchain in the Manufacturing Industry- Key Use Cases, Frankfurt School Blockchain Center (Medium), March 11, 2022.

